Indexed in:
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
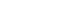
- Preprocedural prognostic nutritional index predicts early gastrointestinal symptoms after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy or percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Yoonhong Kim, Jee Young Lee, Yeajin Moon, Seung Hun Lee, Kyung Won Seo, Ki Hyun Kim
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(3):196-202. Published online December 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0032
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) reflects immunonutritional status and is a well-established predictor of surgical outcomes. Although its association with post-gastrostomy mortality has been documented, its relationship with early gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate whether the preprocedural PNI predicts early GI symptoms following percutaneous gastrostomy, including percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) and percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy (PRG).
Methods
This retrospective study included 71 adults who underwent PEG or PRG. Early GI symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, occurring within 7 days were recorded. The preprocedural PNI, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and the C-reactive protein (CRP)-to-albumin ratio were analyzed using logistic regression to identify predictors. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to assess the PNI’s discriminative performance.
Results
Early GI symptoms occurred in 21 of 71 patients (29.6%). In univariate analysis, the PNI (P=0.009) and CRP-to-albumin ratio (P=0.018) were significant predictors, whereas NLR was not (P=0.125). After adjustment for potential confounders, including age, sex, body mass index, and NLR, the PNI remained an independent predictor of early GI symptoms (adjusted odds ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.83–0.98; P=0.021). ROC analysis for the PNI produced an area under the curve of 0.696, with an optimal cutoff value of 41.3 (sensitivity 70.6%, specificity 66.7%).
Conclusion
A lower preprocedural PNI is independently associated with the development of early GI symptoms after gastrostomy. The PNI may serve as a practical screening tool to identify high-risk patients who could benefit from preemptive nutritional optimization.
- 697 View
- 15 Download

Review
- Efficacy of monounsaturated fatty acids in reducing risk of the cardiovascular diseases, cancer, inflammation, and insulin resistance: a narrative review
- Ki Hyun Kim, Yoonhong Kim, Kyung Won Seo
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2023;15(1):2-7. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2023.15.1.2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: The purpose of this review is to explore the potential benefits of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), specifically those found in olive oil, on weight loss, cardiovascular disease, cancer, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Additionally, this review examines the use of olive oil–based intravenous lipid emulsions (ILEs) in providing parenteral nutrition to patients with diverse needs.
Current concept: MUFAs, found in olive oil, nuts, and some animal foods, have been found to have numerous health benefits. A diet high in MUFAs can aid in weight loss and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Olive oil, in particular, has been linked to a lower risk of cancer, inflammation, and insulin resistance. In addition, olive oil–based ILEs have been utilized for over two decades and are well tolerated by patients requiring parenteral nutrition.
Conclusion: A diet rich in MUFAs, specifically from olive oil, can provide numerous health benefits, including weight loss and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Additionally, olive oil–based ILEs have been shown to effectively provide nutrients to diverse populations requiring parenteral nutrition and have demonstrated the ability to preserve immune function and induce less lipid peroxidation than other ILEs. Further research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits of MUFAs and olive oil-based ILEs, but current evidence suggests that they may be a valuable addition to a healthy diet and medical treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of daily extra virgin olive oil consumption on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jéssica Vidal Damasceno, Anderson Garcez, Andressa Anelo Alves, Isabella Rosa da Mata, Simone Morelo Dal Bosco, Juliano Garavaglia
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2026; 66(2): 392. CrossRef - Applying Wild Mistol Fruits (Sarcomphalus Mistol) from the Paraguayan Chaco as Value-Added Food Ingredients
Villalba R., Belotto J., Coronel E., Carvajal M., Recalde C., Caballero S., Friesen A., Mereles L.
Plant Foods for Human Nutrition.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Key Genes, Metabolites and Pathways Underlying Meat Quality and Intramuscular Fat Deposition Differences Between Tibetan Pigs and Duroc × Tibetan Crossbred Pigs
Junda Wu, Qiuyan Huang, Baohong Li, Zixiao Qu, Xinming Li, Fei Li, Haiyun Xin, Jie Wu, Chuanhuo Hu, Sen Lin, Xiangxing Zhu, Dongsheng Tang, Chuang Meng, Zongliang Du, Erwei Zuo, Fanming Meng, Sutian Wang
Animals.2026; 16(2): 214. CrossRef - The MetaboHealth Score Enhances Insulin Resistance Metabotyping for Targeted Fat Loss: The PERSON Study
Jordi Morwani‐Mangnani, Fatih A. Bogaards, Alexander Umanets, Gabby B. Hul, Anouk Gijbels, Gijs H. Goossens, Joris Deelen, Marian Beekman, Lydia Afman, Ellen E. Blaak, P. Eline Slagboom
Obesity.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the cream composition: Insight into changes of vitamin D3 content and fatty acid composition
Tetiana Dyrda-Terniuk, Viorica Railean, Aleksandra Bogumiła Florkiewicz, Justyna Walczak-Skierska, Mateusz Kolankowski, Joanna Rudnicka, Dorota Białczak, Paweł Pomastowski
International Dairy Journal.2025; 161: 106118. CrossRef - Palmitoleic and oleic fatty acids as biomarkers for coronary heart disease: A predictive model
Guangzhou Wang, Lin Zhou, Zhengfang Wang, Asmaa Ali, Liang Wu
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2025; 194(1): 59. CrossRef - Macrophages: their role in immunity and their relationship with fatty acids in health and disease
Mayte Rueda-Munguía, Luis Alberto Luévano-Martínez, Gerardo García-Rivas, Elena Cristina Castillo, Omar Lozano
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Nutritional Value of Prunus dulcis Blossoms and the Antioxidant Compounds of Their Extracted Oil Using Green Extraction Method
Theodoros Chatzimitakos, Vassilis Athanasiadis, Konstantina Kotsou, Ioannis Makrygiannis, Eleni Bozinou, Stavros I. Lalas
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(5): 2001. CrossRef - Oleic Acid and Succinic Acid: A Potent Nutritional Supplement in Improving Hepatic Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Sprague–Dawley Rats
Kemmoy G. Lattibeaudiere, Ruby Lisa Alexander-Lindo, Mozaniel Oliveira
Advances in Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effects of daily extra virgin olive oil consumption on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 32,430 View
- 91 Download
- 9 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev