Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Preprocedural prognostic nutritional index predicts early gastrointestinal symptoms after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy or percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Yoonhong Kim, Jee Young Lee, Yeajin Moon, Seung Hun Lee, Kyung Won Seo, Ki Hyun Kim
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(3):196-202. Published online December 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0032
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
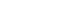
The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) reflects immunonutritional status and is a well-established predictor of surgical outcomes. Although its association with post-gastrostomy mortality has been documented, its relationship with early gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate whether the preprocedural PNI predicts early GI symptoms following percutaneous gastrostomy, including percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) and percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy (PRG).
Methods
This retrospective study included 71 adults who underwent PEG or PRG. Early GI symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, occurring within 7 days were recorded. The preprocedural PNI, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and the C-reactive protein (CRP)-to-albumin ratio were analyzed using logistic regression to identify predictors. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to assess the PNI’s discriminative performance.
Results
Early GI symptoms occurred in 21 of 71 patients (29.6%). In univariate analysis, the PNI (P=0.009) and CRP-to-albumin ratio (P=0.018) were significant predictors, whereas NLR was not (P=0.125). After adjustment for potential confounders, including age, sex, body mass index, and NLR, the PNI remained an independent predictor of early GI symptoms (adjusted odds ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.83–0.98; P=0.021). ROC analysis for the PNI produced an area under the curve of 0.696, with an optimal cutoff value of 41.3 (sensitivity 70.6%, specificity 66.7%).
Conclusion
A lower preprocedural PNI is independently associated with the development of early GI symptoms after gastrostomy. The PNI may serve as a practical screening tool to identify high-risk patients who could benefit from preemptive nutritional optimization.
- 182 View
- 9 Download

- Perioperative outcomes of older adult patients with pancreatic cancer based on nutritional status: a retrospective cohort study
- Takanori Morikawa, Masaharu Ishida, Masamichi Mizuma, Kei Nakagawa, Takashi Kamei, Michiaki Unno
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):66-74. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the effects of preoperative nutritional status on postoperative outcomes in older adult patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Methods
The background and perioperative factors of patients who underwent pancreatectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma between 2007 and 2020 were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
Patients aged 75 years or over (older adults) were significantly associated with hypertension, upfront surgery, and lower prognostic nutritional index. In addition, these patients had a significantly lower rate of portal vein resection, less blood loss, and shorter operation time than patients aged less than 75 years (non-older adults). During the postoperative course, older adult patients had a higher rate of pneumonia and lower overall survival than younger patients, although recurrence‐free survival was comparable. In addition, older adult patients showed preoperative malnutrition as a risk factor for postoperative in‐hospital death.
Conclusion
Surgical treatment for pancreatic cancer in older adult patients was performed safely. However, preoperative malnutrition is a risk factor for in‐hospital death and such patients require nutritional support and less‐invasive surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
Ye Rim Chang
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 95. CrossRef
- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
- 1,571 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Prognostic significance of serum creatinine and sarcopenia for 5-year overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer in Korea: a comparative study
- Jiahn Choi, Hye Sun Lee, Jeonghyun Kang
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(2):66-77. Published online August 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.2.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose: Previous studies have demonstrated that the serum creatinine level and skeletal muscle index (SMI) (correlated with the overall survival [OS] of patients with colorectal cancer [CRC]). However, the combined significance of these 2 factors is not fully understood. The goal of this study was to investigate the prognostic potential of the combination of these two factors in patients with CRC.
Methods: The patients were categorized into subgroups based on preoperative serum creatinine level, with a cut-off value of 1.01 mg/dL for males and 0.80 mg/dL for females. The patients were further categorized into 4 groups based on SMI. Data were analyzed using the Cox proportional hazards model and Harrell’s concordance index (C-index).
Results: Poor 5-year OS was observed in patients with high SMI and high serum creatinine levels (hazard ratio [HR]=1.676, 95% confidence interval [CI]=1.110–2.529, P=0.013), low SMI and low serum creatinine levels (HR=1.916, 95% CI=1.249–2.938, P=0.002), and low SMI and high serum creatinine levels (HR=2.172, 95% CI=1.279–3.687, P=0.004) compared to those of patients with high SMI and low serum creatinine levels. Grouping patients based on both SMI and serum creatinine levels led to improved prognostic stratification (C-index, 0.626; 95% CI=0.587–0.666) compared to grouping based on SMI (CI difference=0.062, 95% CI=0.031–0.103, P=0.0011) or serum creatinine (CI difference=0.043, 95% CI=0.017–0.081, P=0.0072) alone.
Conclusion: Incorporating both SMI and serum creatinine levels enhances the prognostic stratification for 5-year OS in patients with CRC, surpassing the prognostic power of grouping solely based on SMI or creatinine.
- 2,673 View
- 17 Download

- Impact of Visceral Fat Area Measured by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis on Clinico-Pathologic Outcomes of Colorectal Surgery
- Kyeong Eui Kim, Woo Jin Song, Minji Seok, Sung Uk Bae, Woon Kyung Jeong, Seong Kyu Baek
- J Clin Nutr 2021;13(1):17-23. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/jcn.2021.13.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: This study investigated the relationship between the visceral fat area (VFA) and clinico-pathological outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC).
Methods: This retrospective study included 204 patients who underwent anthropometric measurement by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) before surgical treatment for CRC between January 2016 and June 2020.
Results: According to the average value of the visceral fat area, 119 (58.3%) patients had a low visceral fat area, and 85 (59.1%) patients had a high visceral fat area. Patients with visceral obesity showed a higher BMI compared to patients without visceral obesity, (21.8±1.9 vs. 25.7±2.5, P<0.001). There was no significant difference in the overall perioperative outcomes including total operation time, time to gas out, sips of water, soft diet, hospital stay, and morbidity between patients in the low and high VFA groups. We divided patients into two subgroups according to the degree of cancer progression and more advanced cases with low VFA showed significantly more total and positive retrieved lymph nodes (LNs) (20.9±10.3 vs. 16.1±7.1, P=0.021 and 3.3±2.9 vs. 2.2±2.3, P=0.019, respectively) and a higher proportion of more than 12 retrieved LNs compared to patients with a high VFA (95.1% vs. 90.0%, P=0.047). Body composition analysis showed that phase angle, muscle composition, and body fluid composition were not statistically different between the two groups. However, body fat mass was statistically higher in the high VFA group (22.0±4.6 vs. 12.8±3.1, P<0.001).
Conclusion: Visceral obesity measured by BIA showed lower total and positive retrieved LNs and was not associated with adverse peri-operative outcomes, inflammatory and nutritional, and pathologic outcomes for CRC.
- 1,224 View
- 3 Download

- Relationship between Selenium Plasma Levels and Prognosis of Major Burn Patients
- Seung Hyun Hwang, Tae Young Jang, Tae Young Jang, Hye Jung Han, Hye Jung Han, Go Woon Woo, Go Woon Woo
- Surg Metab Nutr 2015;6(2):28-32. Published online December 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2015.6.2.28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose:
Selenium is an important trace element for antioxidative function. Low selenium plasma level in sepsis is associated with high oxidative damage and increasing consumption of selenium, which is thought to affect severity of burns. This study was conducted to investigate a relationship between selenium plasma levels and prognosis of burn patients.
Materials and Methods:
In a retrospective review of 45 burn patients with more than 20% TBSA from January 2011 to May 2015, selenium plasma levels on days 2 to 7 after burn injury, abbreviated burn severity index (ABSI), mortality, length of stay in intensive care unit, and duration of intravenous antibiotics use were measured.
Results:
Selenium plasma levels on days 2 to 7 after burn injury were fairly correlated with ABSI (r=-0.640, P<0.001), TBSA (r=-0.640, P<0.001), duration of intravenous antibiotics use (r=-0.555, P<0.001), and length of stay in intensive care unit (r=-0.445, P=0.004). In comparison between survivor and non-survivor, statistical difference was observed between two selenium plasma levels (66.2±13.6 mcg/L versus 49.4±14.5 mcg/L, P=0.002).
Conclusion:
In this study, selenium plasma levels on days 2 to 7 after burn injury was related to prognosis of major burn patients.
- 498 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev