Indexed in:
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Perioperative nutritional practices and pediatric nutrition support team implementation in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Dayoung Ko, Honam Hwang, Hee-Beom Yang, Joong Kee Youn, Hyun-Young Kim
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(3):181-187. Published online December 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0027
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Purpose
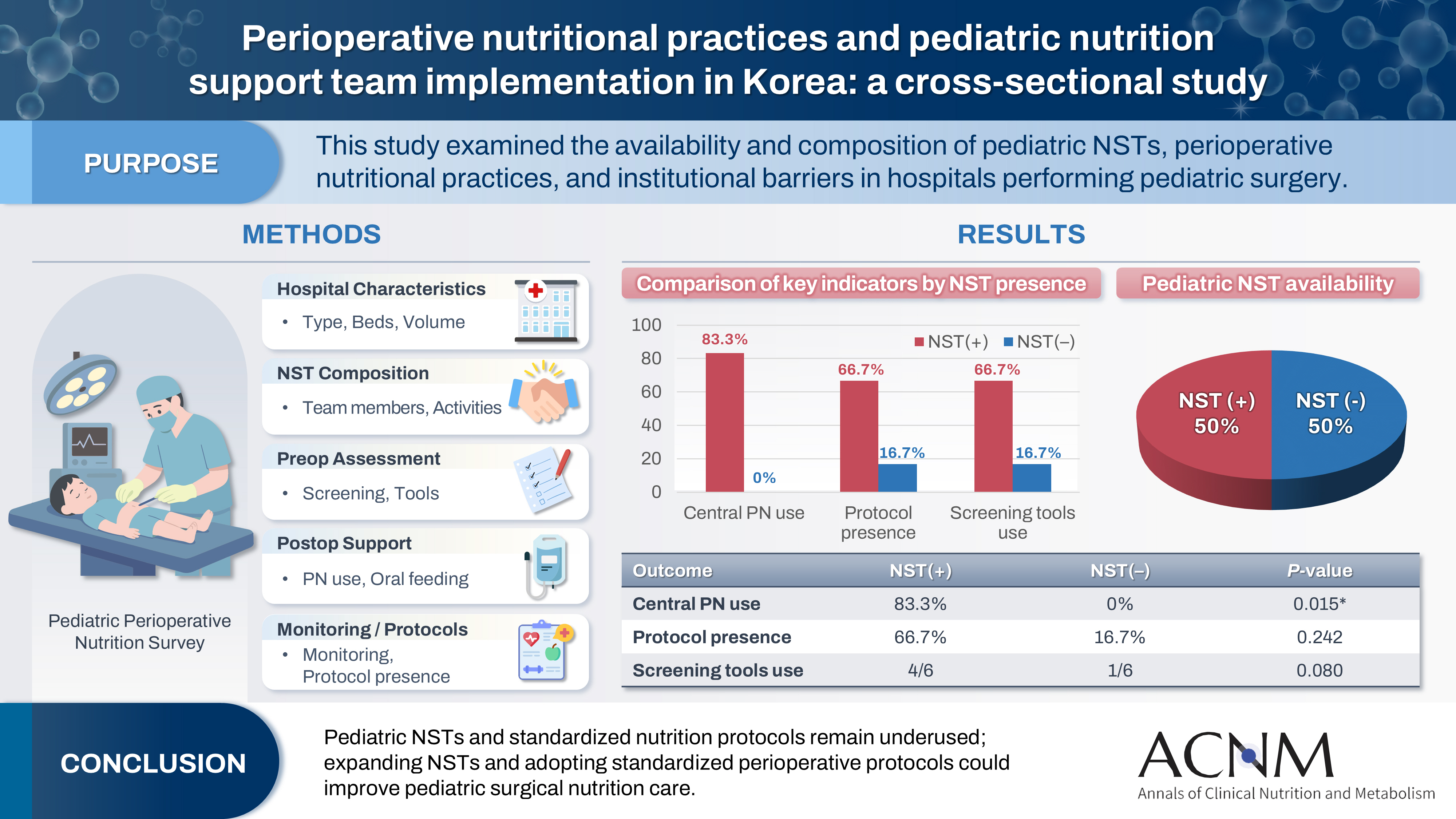
Pediatric surgical patients are vulnerable to perioperative malnutrition, yet standardized nutritional care and structured nutrition support team (NST) involvement remain inconsistent across institutions. Although multidisciplinary nutritional support has gained increasing attention, data on pediatric NST practices within surgical settings in Korea are limited. This study examined the availability and composition of pediatric NSTs, perioperative nutritional practices, and barriers in hospitals performing pediatric surgery.
Methods
A nationwide cross-sectional survey was conducted among tertiary and secondary hospitals that perform pediatric surgery in Korea. The questionnaire assessed hospital characteristics, the presence and composition of pediatric NSTs, perioperative nutritional screening and support practices, monitoring protocols.
Results
A total of 12 hospitals participated. Although all were high-capacity institutions, only half reported having a pediatric NST. Routine preoperative nutritional screening was performed in 50% of hospitals, and validated tools such as Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics (STAMP) and Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score (PYMS) were used in 41.7%. Hospitals with a pediatric NST more frequently had institutional protocols for nutritional evaluation (66.7% vs. 16.7%) and were more likely to administer central venous parenteral nutrition postoperatively (83.3% vs. 0%, P=0.015). Enhanced Recovery After Surgery protocols were implemented in only two hospitals (16.7%). Major barriers to pediatric NST operation included insufficient staffing and time constraints.
Conclusion
Pediatric NSTs and standardized perioperative nutrition protocols remain underutilized in Korean surgical centers. Institutions with a pediatric NST demonstrated more structured nutritional practices. Expanding NST infrastructure and establishing standardized perioperative protocols for pediatric surgical patients may enhance the quality and consistency of nutritional care.
- 892 View
- 16 Download

Guideline
- A practical guide for enteral nutrition from the Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Part I. prescribing enteral nutrition orders
- Ye Rim Chang, Bo-Eun Kim, In Seok Lee, Youn Soo Cho, Sung-Sik Han, Eunjung Kim, Hyunjung Kim, Jae Hak Kim, Jeong Wook Kim, Sung Shin Kim, Eunhee Kong, Ja Kyung Min, Chi-Min Park, Jeongyun Park, Seungwan Ryu, Kyung Won Seo, Jung Mi Song, Minji Seok, Eun-Mi Seol, Jinhee Yoon, Jeong Meen Seo, for KSPEN Enteral Nutrition Committee
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):3-8. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a comprehensive practical guide for enteral nutrition (EN) designed to enhance patient safety and reduce complications in Korea. Under the leadership of the Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (KSPEN), the initiative sought to standardize EN procedures, improve decision-making, and promote effective multidisciplinary communication.
Methods
The KSPEN EN committee identified key questions related to EN practices and organized them into seven sections such as prescribing, delivery route selection, formula preparation, administration, and quality management. Twenty-one experts, selected based on their expertise, conducted a thorough literature review to formulate evidence-based recommendations. Drafts underwent peer review both within and across disciplines, with final revisions completed by the KSPEN Guideline Committee. The guide, which will be published in three installments, addresses critical elements of EN therapy and safety protocols.
Results
The practical guide recommends that EN orders include detailed elements and advocates the use of electronic medical records for communication. Standardized prescription forms and supplementary safety measures are outlined. Review frequency is adjusted according to patient condition—daily for critically ill or unstable patients and as dictated by institutional protocols for stable patients. Evidence indicates that adherence to these protocols reduces mortality, complications, and prescription errors.
Conclusion
The KSPEN practical guide offers a robust framework for the safe delivery of EN tailored to Korea’s healthcare context. It emphasizes standardized protocols and interdisciplinary collaboration to improve nutritional outcomes, patient safety, and operational efficiency. Rigorous implementation and monitoring of adherence are critical for its success. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bridging evidence and clinical practice: a practical guide for enteral nutrition from the Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
Suk-Kyung Hong
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(1): 1. CrossRef
- Bridging evidence and clinical practice: a practical guide for enteral nutrition from the Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
- 6,907 View
- 185 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Efficacy of high-protein diet protocol and education after distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer patients to prevent loss of lean body mass in Korea: a non-randomized controlled study
- Hee Kyung Yoon, Sun Ae Kim, Ji Yoon Han, Dong Jin Kim
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(1):10-19. Published online April 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.1.10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose: We studied whether active education of patients about the importance of a high-protein diet can prevent lean body mass loss after gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Methods: In the study group, intensive high protein diet education and monitoring was performed immediate post operative, 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery. Study group patients were compared with data from the control group formed using propensity matching with the study group for age, sex, resection extent, and TNM stage. Clinicopathologic factors were compared between the groups, and changes in quality of life (QOL) and lean body mass between preoperative levels and 6 months after surgery were assessed.
Results: Among the 100 patients, 31 patients from each group were matched with propensity matching. The groups had no significant clinicopathologic differences. Although the changes in QOL scale and body composition did not differ statistically between the groups, a favorable trend was observed in the study group. Six months after surgery, the mean change in the QOL scale, which measured physical, role, emotional, cognitive, and social functioning, decreased less than the control group or even increased in the study group. In the body composition analysis, the study group showed greater reductions in weight, body mass index, fat mass, and body fat percentage than the control group, and their lean body mass and skeletal muscle mass decreased less.
Conclusion: A high-protein diet protocol and education might increase patient QOL and prevent a decrease in lean body weight 6 months after distal gastric resection.
- 4,518 View
- 42 Download

- Perioperative nutritional practices and attitudes among gastrointestinal oncologic surgeons in Korea: a nation-wide survey study
- Dae Hoon Kim, Jeong-Meen Seo, Min-Gew Choi
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2023;15(3):81-87. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2023.15.3.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the current perioperative nutritional practices and attitudes among gastrointestinal (GI) oncologic surgeons in Korea. Evidence-based perioperative nutritional practices are not well-established in this field.
Methods: A nationwide survey was conducted with 24 items, targeting GI oncologic surgical faculty members from March 2022 to April 2022 through social networking service messaging and email. Whole target number was 3,421.
Results: Out of responding 161 GI surgeons, 83.9% were male and 16.1% were female, and about 49.7% were in their 40s. When asked about their hospital policies, 67.1% reported the existence of formal nutritional screening programs. However, the execution and analysis of these programs varied considerably. Most surgeons conducted preoperative nutritional screening, with albumin testing the most frequently performed. In addition, nutritional supplementation—primarily protein drinks—was given before surgery. The duration for which these supplements were used varied from ≤3 days to 4–7 days. Most respondents recognized the importance of addressing nutritional deficiencies in patients with GI tumors; however, when asked about immunonutrition, 89.4% of surgeons admitted having limited knowledge.
Conclusion: Although there is recognition of the importance of evidence-based nutrition practices in GI and oncologic surgery programs, this study reveals limited implementation of such practices. This study highlights a considerable opportunity to leverage existing positive surgeon beliefs and published data on the benefits of perioperative nutrition to enhance surgical nutrition practices and to improve patient outcomes in Korea.
- 1,432 View
- 10 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev